Facts About Rhinoplasty - Rush System Revealed
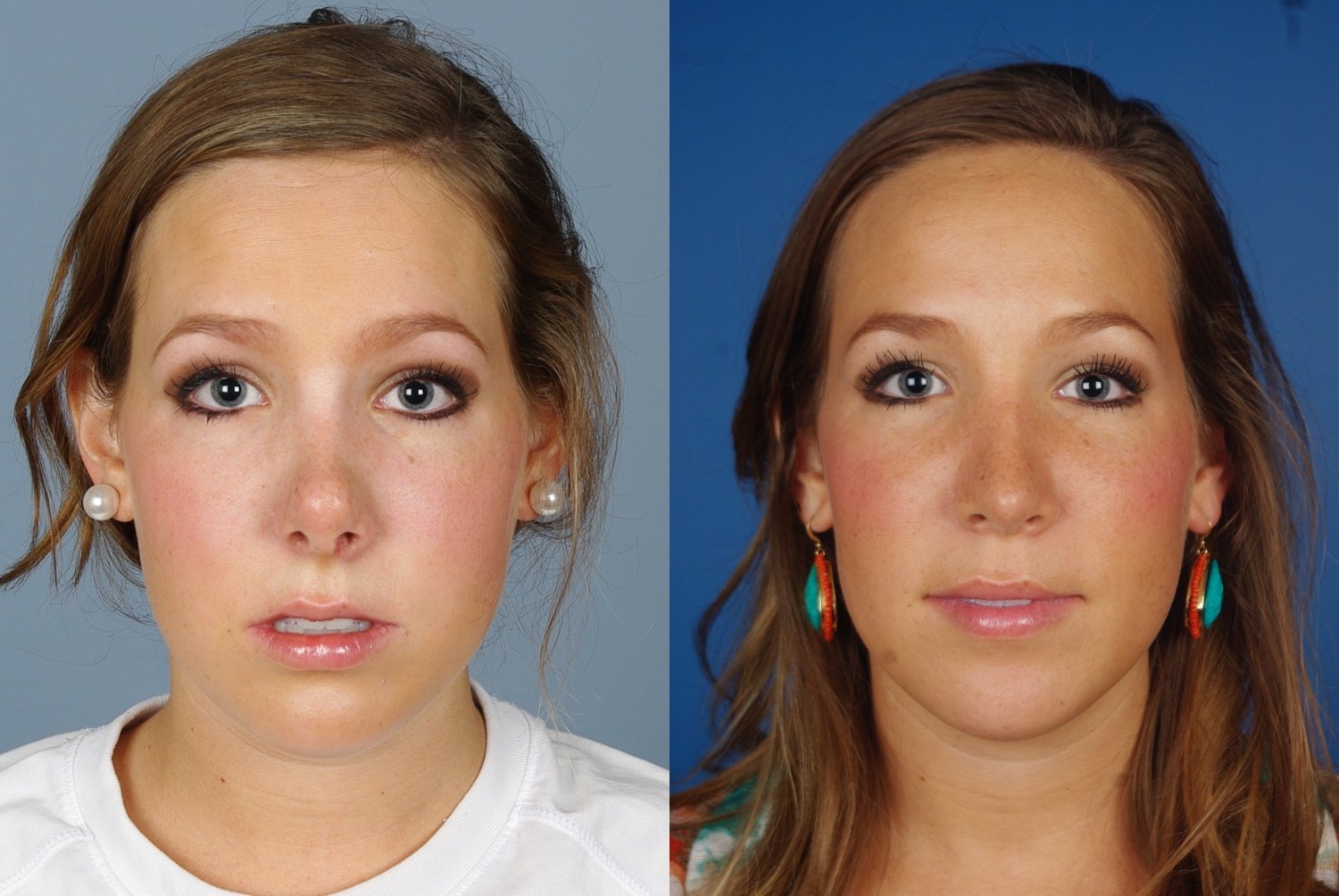 Nasal Surgery (Rhinoplasty) - Pinehurst Surgical Clinic
Nasal Surgery (Rhinoplasty) - Pinehurst Surgical ClinicIndicators on New York Rhinoplasty & Nose Job Expert - DrPhilip Miller You Need To Know
the elevator muscle group that includes the procerus muscle and the levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle. the depressor muscle group which includes the alar nasalis muscle and the depressor septi nasi muscle. the compressor muscle group that includes the transverse nasalis muscle. the dilator muscle group that includes the dilator naris muscle that broadens the nostrils; it is in two parts: (i) the dilator nasi anterior muscle, and (ii) the dilator nasi posterior muscle.

B. Visual appeal of the nose nasal subunits and nasal segments [edit] To prepare, map, and perform the surgical correction of a nasal problem or defect, the structure of the external nose is divided into 9 aesthetic nasal subunits, and six visual nasal segments, which offer the plastic surgeon with the steps for figuring out the size, level, and topographic area of the nasal defect or defect.
 Rhinoplasty West Palm Beach, FL - Nose Job - Michael Schwartz, MD
Rhinoplasty West Palm Beach, FL - Nose Job - Michael Schwartz, MDRhinoplasty Surgery Effectiveness, Risks, and Side Effects for Beginners
the dorsal nasal sector the lateral nasal-wall segments the hemi-lobule segment the soft-tissue triangle sections the alar sections the columellar sector Nose surgery: The Common carotid artery. Utilizing the co-ordinates of the subunits and sections to figure out the topographic place of the flaw on the nose, the cosmetic surgeon plans, maps, and executes a rhinoplasty treatment.
Thus, if more than half of a visual subunit is lost (harmed, faulty, destroyed) the surgeon changes the entire visual section, typically with a local tissue graft, gathered from either the face or the head, or with a tissue graft harvested from in other places on the patient's body. C. Key Reference and veins [modify] Like the face, the human nose is well vascularized with arteries and veins, and therefore supplied with plentiful blood.
10 Easy Facts About Rhinoplasty Newport Beach - Nose Surgery Beverly Hills Shown
The external nose is provided with blood by the facial artery, which becomes the angular artery that courses over the superomedial element of the nose. The sellar area (sella turcica, "Turkish chair") and the dorsal area of the nose are supplied with blood by branches of the internal maxillary artery (infraorbital artery) and the ophthalmic arteries that derive from the internal common carotid artery system.
