The Facts About Ontology, Semantic Web and Electronic Government (English) Uncovered
 The Semantic Web
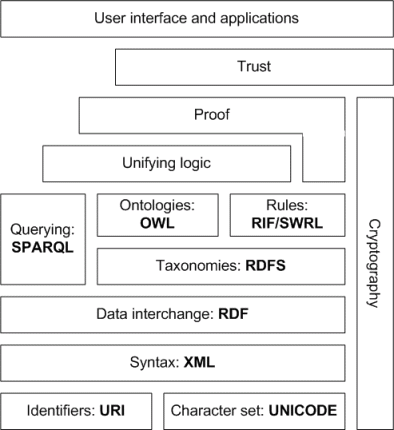
The Semantic Web Semantic Web Layer Cake Tweak, Explained - by Kingsley Uyi Idehen - OpenLink Software Blog - Medium
Semantic Web Layer Cake Tweak, Explained - by Kingsley Uyi Idehen - OpenLink Software Blog - MediumRumored Buzz on The Semantic Web: An Introduction - infomesh.net
g. a text, a number, etc). Research It Here lead to the graph shown in the provided figure. Graph arising from the RDFa example, improved with further information from the Web Among the advantages of using Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) is that they can be dereferenced using the HTTP protocol.
In this example, all URIs, both for edges and nodes (e. g. http://schema. org/Person, http://schema. org/birth, Location, http://www. http://wikidata.org/entity/Q1731) can be dereferenced and will lead to additional RDF graphs, describing the URI, e. g. that Dresden is a city in Germany, or that an individual, in the sense of that URI, can be imaginary.
org/Person (green edge) and https://www. http://wikidata.org/entity/Q1731 (blue edges). Additionally to the edges given in the included documents clearly, edges can be instantly presumed: the triple from the initial RDFa piece and the triple from the file at https://schema. org/Person (green edge in the figure) permit to infer the following triple, offered OWL semantics (red dashed line in the second Figure): Background [edit] The idea of the semantic network model was formed in the early 1960s by scientists such as the cognitive researcher Allan M.

Ross Quillian and psychologist Elizabeth F. Loftus as a form to represent semantically structured understanding. When applied in the context of the modern internet, it extends the network of hyperlinked human-readable websites by placing machine-readable metadata about pages and how they belong to each other. This allows automatic representatives to access the Web more intelligently and carry out more jobs on behalf of users.
The Semantic Web: Two Decades On - Aidan Hogan Fundamentals Explained
He specifies the Semantic Web as "a web of information that can be processed directly and indirectly by devices". Many of the technologies proposed by the W3C already existed before they were positioned under the W3C umbrella. These are used in different contexts, particularly those handling information that includes a restricted and specified domain, and where sharing data is a common need, such as clinical research or data exchange among services.
Limitations of HTML [edit] Lots of files on a common computer system can likewise be loosely divided into human-readable files and machine-readable information. Documents like mail messages, reports, and brochures are read by people. Information, such as calendars, address books, playlists, and spreadsheets exist utilizing an application program that lets them be seen, searched, and integrated.
