All about What Is DHT & How Does It Affect Hair Growth? - Nutrafol
 THE TRUTH BEHIND DHT BLOCKERS- PROS & CONS! - AHS India
THE TRUTH BEHIND DHT BLOCKERS- PROS & CONS! - AHS IndiaThe Greatest Guide To Assessment of the usefulness of dihydrotestosterone in - NCBI
Unfavorable results consist of a loss of libido, a lowered ability to develop and maintain an erection, and a decline in ejaculate. More Details proposed to discuss male pattern hair loss is that, with age, the roots themselves come under increasing pressure from the scalp. In more youthful people, the hair follicles are buffered by the surrounding fat tissue under the skin.
As the skin ends up being dehydrated, the scalp compresses the roots, causing them to lessen. Testosterone likewise contributes to a reduction in the fat tissue, so higher levels of testosterone might further lower the scalp's capability to buffer the hair roots. As follicles attempt to keep their status,, extra enzyme activity takes place in the site.
Further examination of DHT and male pattern baldness may one day enable scientists to lastly break the code of male pattern baldness. For now, it is a waiting video game.
 12 Most Powerful Natural DHT Blockers that Stop Hair Loss - Ak Clinics
12 Most Powerful Natural DHT Blockers that Stop Hair Loss - Ak ClinicsNot known Details About Dht Holdings Stock Price - Barchart.com

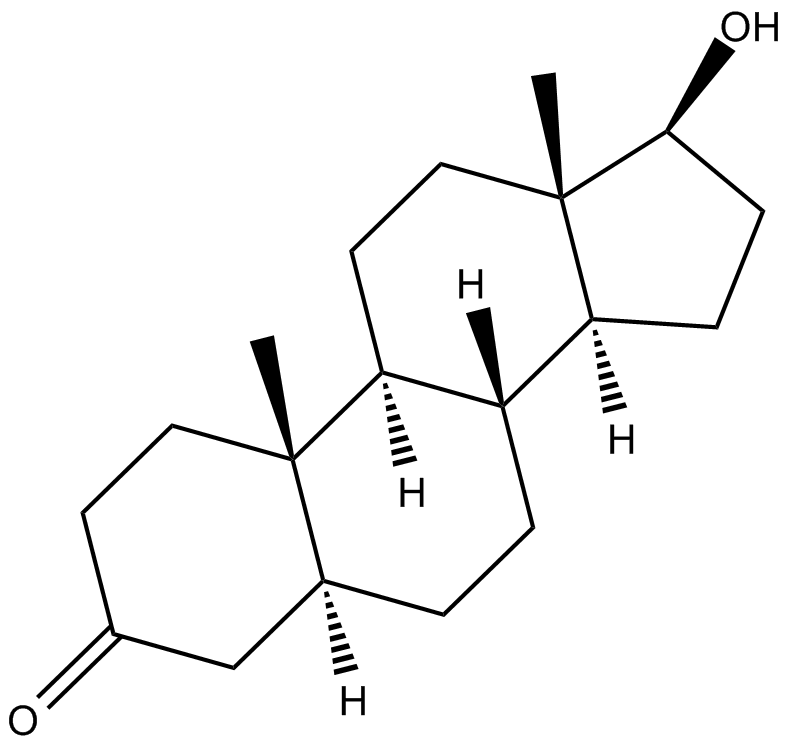
Human hormone Dihydrotestosterone Names (1ST,3 a, S,3 b, R,5 a, S,9 a, S,9 b, S,11 a, S)-1-Hydroxy-9a,11 a-dimethylhexadecahydro-7H-cyclopenta [a] phenanthren-7-one Other names DHT; 5-Dihydrotestosterone; 5-DHT; Androstanolone; Stanolone; 5-Androstan-17-ol-3-one Identifiers In, Ch, I=1S/C19H30O2/c1 -18 -9 -7 -13( 20 )11-12( 18 )3-4-14-15-5-6-17( 21 )19(15,2)10-8-16( 14 )18/h12,14 -17,21 H,3-11H2,1 -2 H3/t12 -,14 -,15 -,16 -,17 -,18 -,19-/ m0/s1 YKey: NVKAWKQGWWIWPM-ABEVXSGRSA-N Y O=C4C [C@@H] 3CC [C@@H] 2 [C@H] (CC [C @] 1(C) [C@@H] (O)CC [C@H] 12) [C@@] 3(C)CC4 Characteristics C19H30O2 290. 447 gmol1 Pharmacology A14AA01 () Transdermal (gel), in the cheek, under the tongue, intramuscular injection (as esters) Pharmacokinetics: Oral: really low (due to substantial very first pass metabolism) Other than where otherwise noted, information are provided for materials in their standard state (at 25 C [77 F], 100 k, Pa).
The enzyme 5-reductase catalyzes the formation of DHT from testosterone in certain tissues consisting of the prostate gland, seminal vesicles, epididymides, skin, hair follicles, liver, and brain. This enzyme mediates reduction of the C4-5 double bond of testosterone. Relative to testosterone, DHT is substantially more powerful as an agonist of the androgen receptor (AR).
Biological function [modify] DHT is biologically essential for sexual differentiation of the male genitalia during embryogenesis, maturation of the penis and scrotum at puberty, growth of facial, body, and pubic hair, and development and upkeep of the prostate gland and influential vesicles. It is produced from the less powerful testosterone by the enzyme 5-reductase in select tissues, and is the primary androgen in the genitals, prostate gland, seminal vesicles, skin, and hair roots.
