The Best Strategy To Use For Caffeine Addiction Calendar 12+ - App Store - Apple
Little Known Facts About How to Overcome Caffeine Addiction (with Pictures) - wikiHow.
What is caffeine? Caffeine is the stimulant in your coffee, tea, chocolate and soda that minimizes fatigue, increases awareness and provides you a boost of energy. It can likewise trigger insomnia, headaches, dehydration and high blood pressure, if you're not cautious. For numerous, caffeine is a tool to help them get up, liven up and concentrate.
 Caffeine craze: caffeine addiction is a growing problem among students – BVSW News
Caffeine craze: caffeine addiction is a growing problem among students – BVSW NewsCaffeine is a white, bitter compound that's found naturally in over 60 plants, including coffee beans, tea leaves and cacao pods that are utilized to make chocolate. The U.S. Fda (FDA) considers caffeine to be both a food additive and a drug. The amount of caffeine in your food and drink differs.
 The Truth About ADHD and Addiction
The Truth About ADHD and AddictionCoffee can have just two milligrams of caffeine (decaf coffee) per cup, and as much as 200 milligrams per cup. Your typical tea has about 40 milligrams of caffeine, but it can vary from nine to 110 milligrams. Twelve ounces of soda pop/soft beverage generally has 30 to 60 milligrams of caffeine.
What impact does caffeine have on the body? Caffeine passes into your blood stream from your stomach and little intestinal tract. When in your bloodstream, caffeine promotes your main nervous system your nerves, brain and spinal cable to make you feel more awake and alert. Caffeine lowers tiredness and enhances focus and concentration.

Get This Report on The Dangers Of Abusing Caffeine Pills - Vertava Health
When you consume or eat caffeine, the dopamine signaling in your brain is boosted. Dopamine is a chemical that helps with managing motivation, feelings and movement. You feel more alert and awake when the signaling increases. How This Is Cool is too much? The average American adult consumes 200 mg of caffeine a day.
 Caffeine Addiction Cure: Overcoming The Caffeine Blues Permanently for a Happy, Healthy Life (Caffeine Addiction, Caffeine Blues, Stimulant, Addicted To, Coffee, Coffee Addiction, Coffee Recipes) - Kindle edition by Cook, GregHealth,
Caffeine Addiction Cure: Overcoming The Caffeine Blues Permanently for a Happy, Healthy Life (Caffeine Addiction, Caffeine Blues, Stimulant, Addicted To, Coffee, Coffee Addiction, Coffee Recipes) - Kindle edition by Cook, GregHealth,Taking in up to 400 mg or four cups of coffee does not trigger problems for the majority of people. However, caffeine impacts people differently, depending upon their size, gender and sensitivity to it. If you're delicate to caffeine, even moderate amounts can cause insomnia (problem sleeping), rapid heart rate, anxiety and sensations of uneasyness.
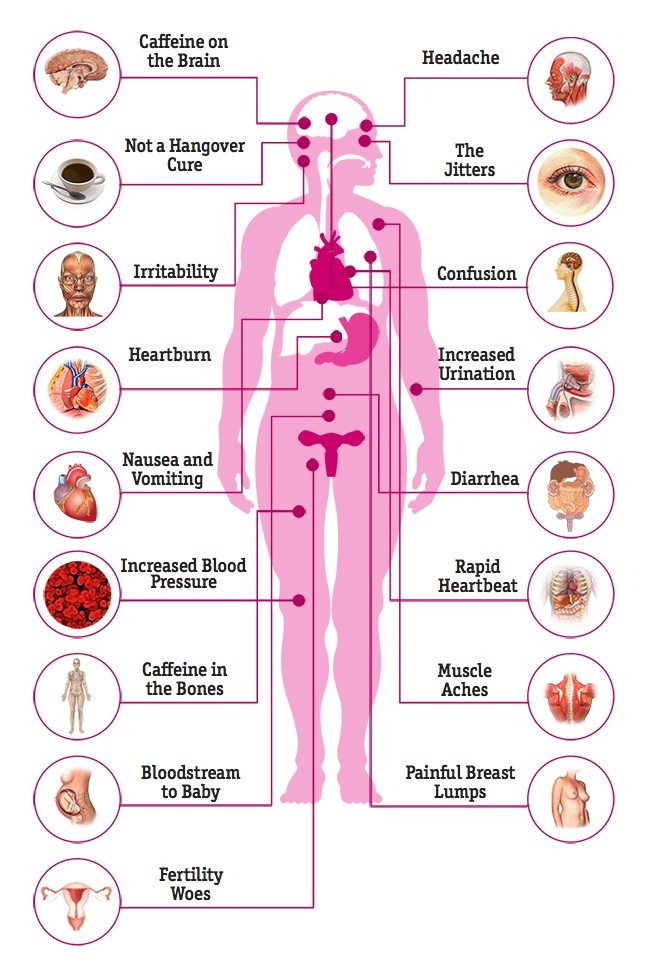
What are the symptoms of having excessive caffeine? Signs of having too much caffeine might include: Headache, nervousness, dizziness. Having "the jitters" or feeling shaky. Insomnia or sleep that is "on and off" throughout the night. Racing heart or unusual heart beat. Increase in high blood pressure. Dehydration. Who should avoid caffeine? It's not safe for everyone to have caffeine in their diet.
