The 2-Minute Rule for How to Use Modes: A Guide For Bass Players - Online Bass
Some Ideas on Doric® Lydian Copper Concrete Vault - Lake Shore Funeral You Need To Know
One example: C, D, E, F, G, A, B F, G, A, B, C, D, E. The ancient heritage The Lydian Scale emerged in the ancient Greece together with other scales such as Locrian and Phrygian. The names were drawn from areas or individuals the Lydians once lived in western Anatolia.
These correspond the Lydian except for the raised second and raised 5th. Notification that the Lydian #2 is relative to the Melodic Minor. A 3rd transformed Lydian scale is the Lydian b7 (flat seven), likewise referred to as Lydian Dominant and pointed out above. These are all modified Lydian scales.
8 Easy Facts About Shop Dixie Home Morning Mist Lydian 556346134 Carpet - Great Described
10 May 2021, 16:45 From their significance to their history in Western music, here's an easy guide to modes. The word 'mode' comes from the Latin for 'manner, or method' however musical modes all stem in ancient Greece, so they have Greek names. The modes were called after numerous areas, possibly to represent individuals who lived there, due to the fact that Greek musical theorists were theorists too, and associated the arts with aspects of morality.
 Marble stele with a Lydian inscription - Lydian - Archaic - The Metropolitan Museum of Art
Marble stele with a Lydian inscription - Lydian - Archaic - The Metropolitan Museum of ArtAlter just one of those notes and you can call your scale a 'mode'. Long prior to people began considering pieces of music having 'secrets', each mode is thought to have actually begun on a various note of the scale, providing its own character to the set of notes running, for example, C to C (Ionian mode) or E to E (Phrygian mode) and so on.
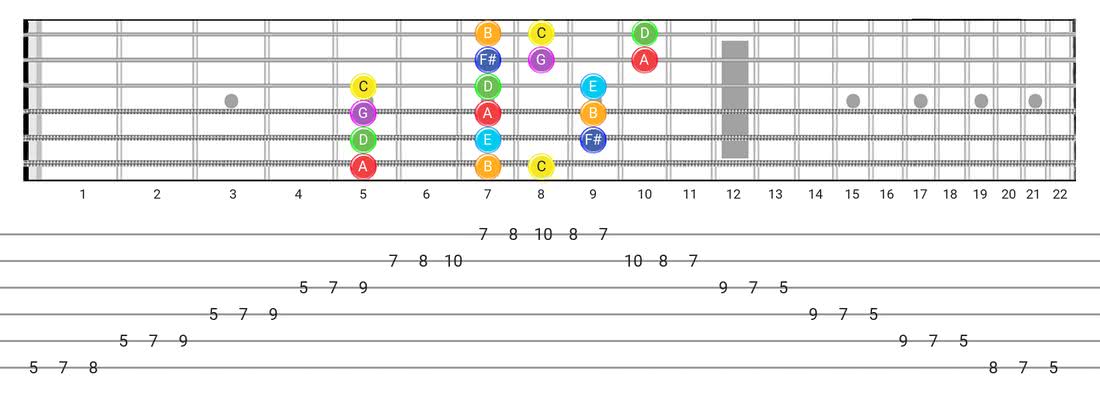 Lydian Chord Progression – How To Play In Lydian? [2021]
Lydian Chord Progression – How To Play In Lydian? [2021]Outsourcing - Global Guide - Practical Law Fundamentals Explained
So, the list goes: Ionian, Dorian, Phrygian, Lydian, Mixolydian, Aeolian and Locrian. Some of them are major modes, some are small, and some are ambiguous. Some modes are sadder or holier than others. The Ionian mode is a simple 'doh re mi' major key. It is the modern significant scale.
A case in point of music in the Ionian mode would be Mozart's Flute and Harp Concerto in C major, or Vivaldi's Mandolin Concerto in C major. More Discussion Posted Here is really comparable to the contemporary natural minor scale. The only distinction remains in the 6th note, which is a major 6th above the very first note, rather than a minor sixth.

